Linear Lights Sweeping the Lighting Market: A Comprehensive Analysis
In the ever-changing world we live in, advanced technology has been consistently enhancing our standard of living and improving our quality of life. Among numerous technological advancements, linear lighting plays an indispensable role in our lives. Linear lighting, a lighting method with a linear shape, has shone brilliantly in countless indoor and outdoor settings, serving as a symbol of fashion and efficiency. This article will delve into the definition, structure, applications, advantages, and disadvantages of linear lighting, granting us a more profound understanding of this unique lighting method.
1. Definition of Linear Lighting
As its name suggests, linear lighting is a type of lighting device that comes in a linear shape, mainly referring to LED linear lighting. With high-quality LED light sources, it possesses the features of high efficiency, durability, and energy saving, making it perform exceptionally well in fields such as urban landscape lighting, architectural lighting, and home lighting. Compared with traditional lighting methods, linear lighting has more advantages and has become the new darling of the lighting market.
2. Structure of Linear Lighting
Linear lighting mainly consists of the following components:
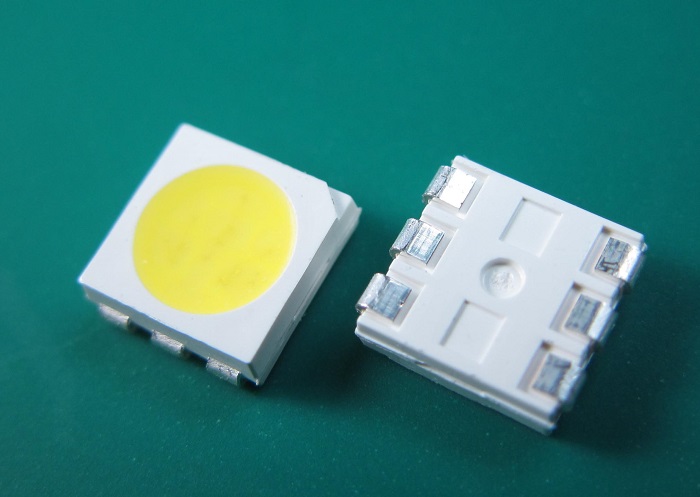
Light source: The core component of linear lighting, responsible for generating light. Currently, common lighting sources in the market include SMD, COB, 2835, 3528, and 5050.
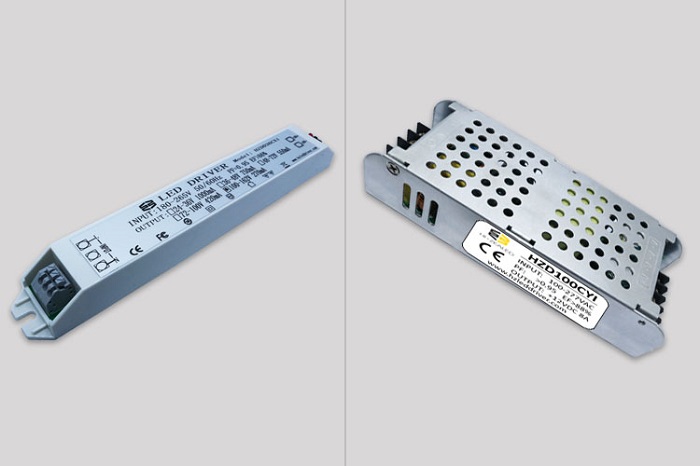
Driver power: Provides power supply and drivers the light source to emit light. The drive device is generally divided into two types: constant current drive and constant voltage drive, and different driving methods have a significant impact on the performance and stability of linear lighting.
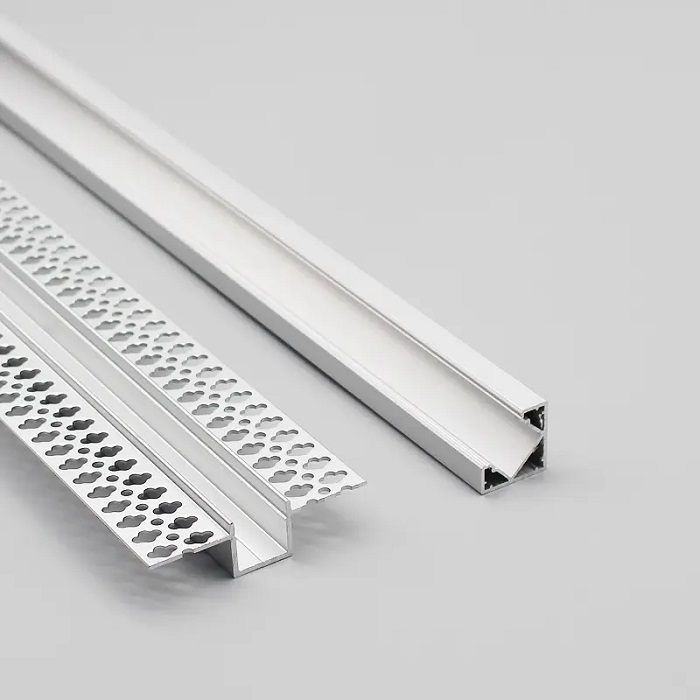
Heat dissipation system: As linear lighting generates a certain amount of heat during operation, a heat dissipation system is essential to ensure its normal operation and prolong its service life. The heat dissipation system of linear lighting mainly includes heat sinks, thermal paste, and aluminum substrates.
Casing: The casing of linear lighting protects the LED light source and the drive device, generally made of high-quality materials such as aluminum, iron, and plastic. Some linear lighting products also have waterproof and dustproof treatments to meet outdoor requirements.
Control system: The control system of linear lighting achieves various control effects, such as color changing, dimming, and cascade, through devices such as controllers and sensors.
3. Applications of Linear Lighting
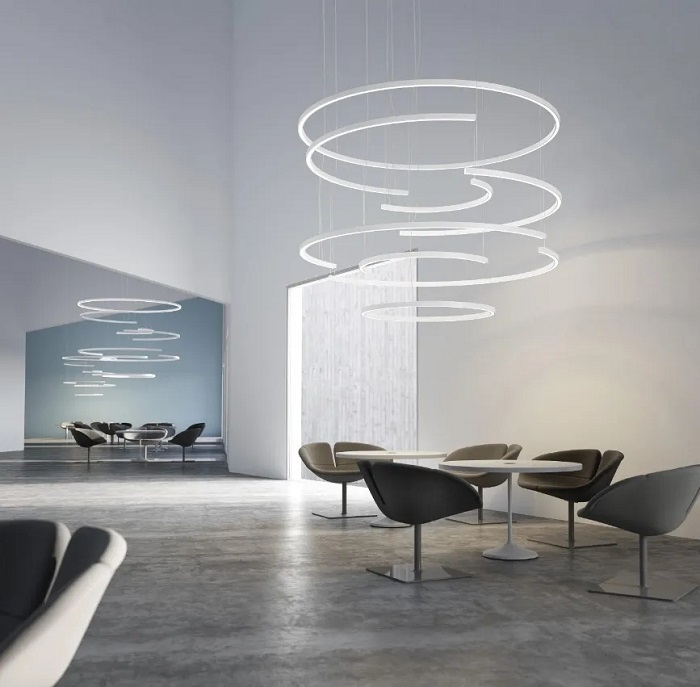
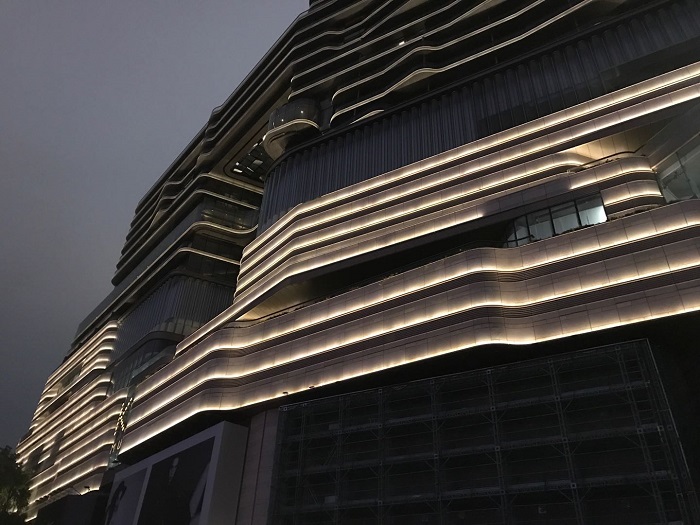
Architectural lighting: Lighting designers often use linear lighting to create an atmosphere full of light and shadow effects, highlighting the architectural features and aesthetic value of buildings, such as enterprises, office buildings, and hotels.
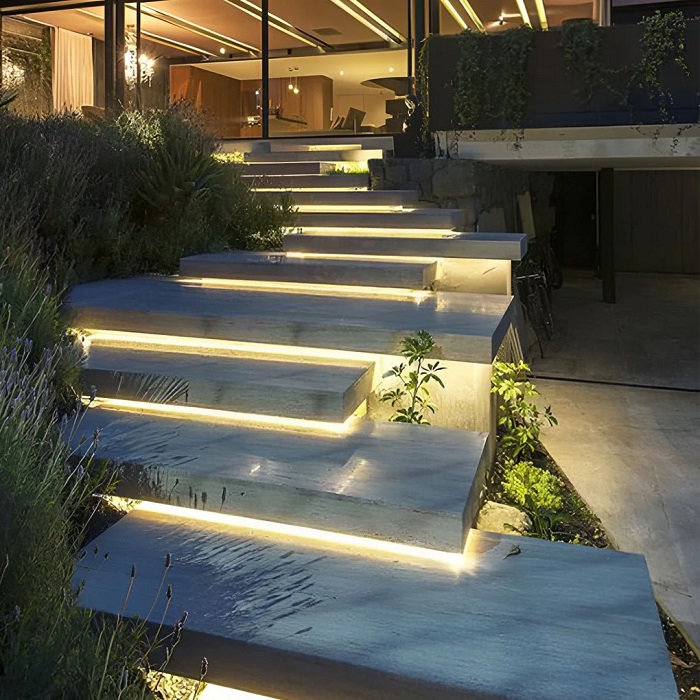
Urban landscape lighting: Linear lighting is widely used in landscape projects such as urban squares, pedestrian streets, parks, and bridges, emphasizing linearity and spatial relationships and enriching the visual experience of the city.
Indoor lighting: The diverse designs and excellent lighting effects of linear lighting make it shine in the field of indoor lighting. Form home lighting to commercial places, exhibitions, conferences, and other occasions, linear lighting can provide the right light source.
Special lighting: In scenes such as production lines and medical equipment, there are strict requirements for light sources. Linear lighting, with its precise light source and energy-saving and environmentally friendly advantages, meets these special needs.
4. Advantages and Disadvantages of Linear Lighting
Advantages:
Energy-saving and environmentally friendly: LED linear lighting has high luminous efficacy and low power consumption, which can save more energy and reduce carbon emissions.
Long lifespan: The service life of LED linear lighting is significantly longer than that of traditional lighting devices, which reduces maintenance costs and improves the durability of the lighting.
High-quality light: LED linear lighting produces high-quality light, with high color rendering index, high uniformity, and no glare, providing a comfortable and bright visual environment.
Disadvantages:
Heat dissipation problem: The heat generated by the LED linear lamp during use needs to be solved, otherwise it will affect its working performance and service life. Fortunately, technology continues to develop, and this problem has been well solved.
In short, as a lighting method, linear lights have unique advantages, and they have a wide range of application prospects no matter in home lighting, commercial lighting or outdoor lighting. With the further development of LED technology, the functions of linear lights will be more abundant, and the designs will be more diversified, bringing us a better light.